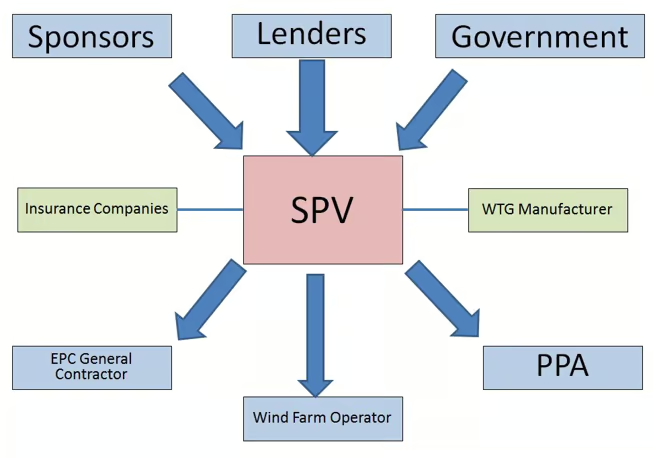
Project Finance
Definition: Project finance is a long-term financing structure used to fund large-scale infrastructure or industrial projects, where lenders primarily rely on the project’s future cash flows as the main source of repayment—rather than the sponsor’s balance sheet or existing assets.
In Simple Words
Project financing refers to the technique of financing where the lenders depend on:
- The cash flows generated by the project itself
- The assets of the project
…as the key sources of loan repayment—not the financials of the parent company (sponsor).
Key Features
- The project is often structured as a separate legal entity (Special Purpose Vehicle – SPV)
- Non-recourse or limited-recourse financing is used (lenders have no or limited claim on sponsor assets)
- Used for large-scale, capital-intensive projects like roads, power plants, airports, etc.
- Risk is allocated to parties best able to manage them (contractors, insurers, government, etc.)
- Funding depends heavily on feasibility, contracts, and revenue certainty
Did You Know? A well-structured and economically viable project can attract long-term financing—even when:
- The project size is larger than the sponsor’s own financial capacity
- The sponsor is unable to bear the risks alone
Key Takeaway
In project finance, existing corporate balance sheets or previously owned assets do not significantly influence the decision-making for new projects. Lenders are primarily focused on whether the new project will generate sufficient cash flows to pay off the loans.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Project Finance
Advantages of Project Finance
- Limited/Non-Recourse Financing: Lenders have claims only on project assets, not sponsors’ balance sheets.
- Risk Allocation: Risks are distributed among sponsors, lenders, contractors, and off-takers.
- Off-Balance-Sheet Treatment: Debt does not appear on sponsors’ financial statements.
- Access to Large Capital: Enables funding for mega-projects without overleveraging sponsors.
- Long-Term Financing: Matches project lifespan (e.g., 20–30 years for infrastructure).
- Tax Benefits: SPVs may optimize tax (e.g., depreciation, interest deductions).
- Asset Isolation: Protects sponsors from project failure via SPV structure.
- Attracts Diverse Investors: Pension funds, DFIs, and private equity can participate.
Disadvantages of Project Finance
- High Transaction Costs: Legal, advisory, and due diligence fees increase upfront expenses.
- Complex Structuring: Requires lengthy negotiations and multiple contracts (PPAs, EPC, etc.).
- Higher Cost of Capital: Lenders charge higher interest rates due to perceived risk.
- Inflexibility: Rigid contracts make it hard to adapt to changes (e.g., demand shifts).
- Political/Regulatory Risks: Vulnerable to policy changes, expropriation, or permit delays.
- Heavy Reliance on Contracts: Failure of any party (e.g., off-taker) can collapse the project.
- Limited Exit Options: Equity is illiquid until project completion/refinancing.
- Construction/Operational Risks: Delays or cost overruns strain cash flows.
Corporate Finance vs Project Finance
| Parameter | Corporate Finance | Project Finance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financing based on the overall creditworthiness of a company. | Financing based on the cash flows and assets of a specific project (e.g., infrastructure). |
| Recourse | Full recourse to the company’s assets and balance sheet. | Limited or non-recourse (lenders can only claim project assets, not sponsors’ other assets). |
| Risk Allocation | Risks borne by the company. | Risks allocated to different parties (EPC contractors, operators, off-takers). |
| Collateral | Company’s existing assets (e.g., factories, receivables). | Only project assets (e.g., toll road, power plant). |
| Debt Tenure | Short to medium term (5–10 years). | Long term (15–30 years), matching project life. |
| Cash Flow Dependence | Relies on the company’s overall financial health. | Relies solely on the project’s revenue (e.g., toll collections, power sales). |