Cash Flow Statement
A Cash Flow Statement is a financial report that provides a summary of the cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving a company during a specific period. It reflects the company’s liquidity and ability to generate cash to fund operations, pay debts, and invest in future growth.
Purpose of Cash Flow Statement
- To assess the ability of a company to generate future cash flows
- To evaluate the company's ability to meet its financial obligations
- To determine how a company finances its operations and growth
- To understand cash movements from operating, investing, and financing activities
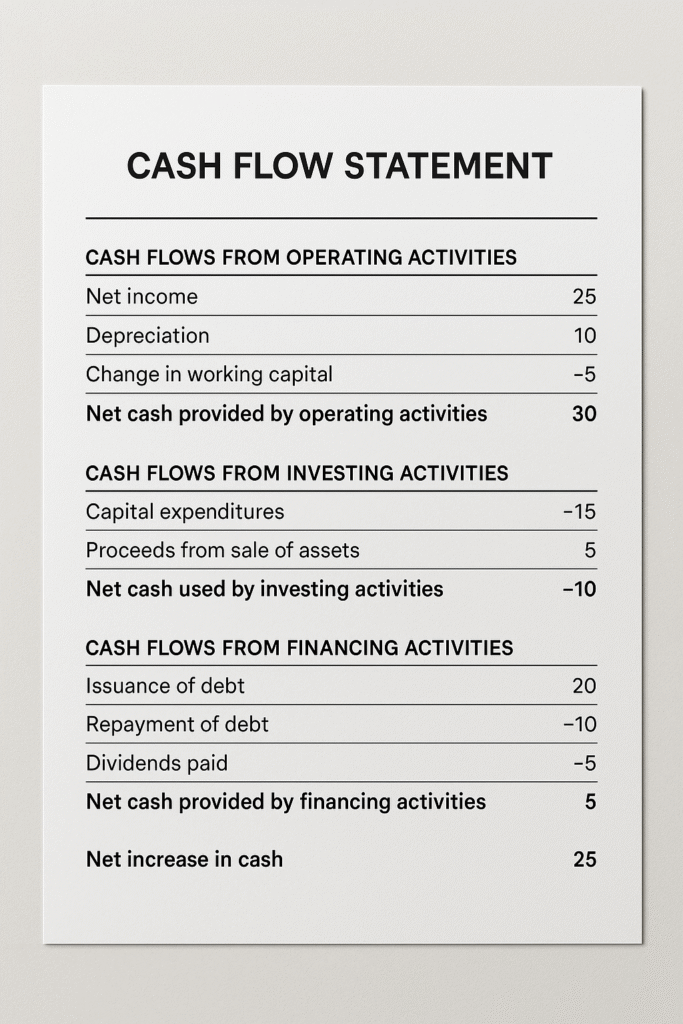
Components of a Cash Flow Statement
1. Operating Activities
Cash flows related to the core business operations such as:
- Cash receipts from sales of goods and services
- Payments to suppliers and employees
- Interest and income tax payments
2. Investing Activities
Cash flows from acquisition or disposal of long-term assets:
- Purchase or sale of property, plant, and equipment (PPE)
- Investments in securities
- Loans made or received
3. Financing Activities
Cash flows that result in changes in the size and composition of equity and borrowings:
- Issuance or repurchase of shares
- Proceeds from loans or repayment of borrowings
- Dividend payments
Importance of Cash Flow Statement
- Helps investors assess a firm’s financial health and liquidity
- Reveals how a company manages its cash in daily operations
- Assists lenders in evaluating creditworthiness
- Supports internal management decisions related to cash control and budgeting
Cash Flow vs. Profit
While profit shows the overall financial performance (revenue - expenses), cash flow reflects the real cash position of a business. A company can be profitable yet face liquidity issues if cash flow is poor.
Conclusion
The cash flow statement is an essential tool in financial analysis. Along with the income statement and balance sheet, it gives a comprehensive view of a company's financial stability.